Build an Online Reporting Application Using Oracle XML Publisher
by Mark Rittman 
Learn how to create an online reporting environment using XML Publisher technology, step by step.
Published June 2006
Part of the Oracle Fusion Middleware family of products, Oracle XML Publisher 5.6.2 is a Java-based product that gives you the ability to define, publish, secure and schedule reports built using SQL and XML data sources. Originally developed as a technology within E-Business Suite, Oracle XML Publisher is now available for download as a stand-alone product, and can be deployed using J2EE application servers such as Oracle Application Server Containers for J2EE (OC4J) or Apache Tomcat. Best of all, XML Publisher uses familiar desktop tools such as Microsoft Word and Adobe Acrobat to define report layouts, meaning that users can design their reports in a familiar environment without having to install and learn a whole new toolset.
XML Publisher consists of a server-based reporting engine that brings together report templates, the data that you wish to report on and any language translations, and then distributes the output in standard formats such as Adobe PDF, HTML, XML, RTF or Microsoft Excel.

Creating a clear separation between data, layout, and interface makes it easier to report the same data in different formats, easier to maintain a library of report definitions, and more straightforward to introduce features such as multiple language translation. XML Publisher is a standalone product that, like the rest of Oracle Fusion Middleware architecture, is “hot-swappable” and integrates with any standards-based database or Java application server.
New with the 5.6.2 release of XML Publisher is XML Publisher Enterprise, a complete environment for deploying, scheduling, and securing your reports. XML Publisher Enterprise provides users with a Web portal where they can upload their report templates, publish them, and then make them available to other users and groups within the organization.
XML Publisher uses a scheduling engine based on the OpenSymphony Quartz scheduler to run and then deliver reports that can then be accessed online, via email or via a WebDAV-enabled server.
So, now that XML Publisher 5.6.2 Enterprise is available, how can you use it to build an online reporting application?
Background
In this example, you will create an online reporting environment for your organization. You will create the initial set of reports that your colleagues will use, and you users will then maintain them and create ones of their own. Key requirements are that the reporting environment is Web-based, secure, and easy for users to navigate and use, reports can be run on demand or scheduled for regular execution, and users can export the data from their reports into familiar desktop application formats such as Microsoft Excel and Adobe Acrobat.
Your initial audience for reports consists of purchasing department users, who wish to view reports on vendor invoices, and a sales manager, who wishes to analyze sales data within his Web browser and through Microsoft Excel.
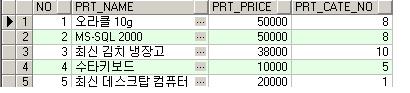
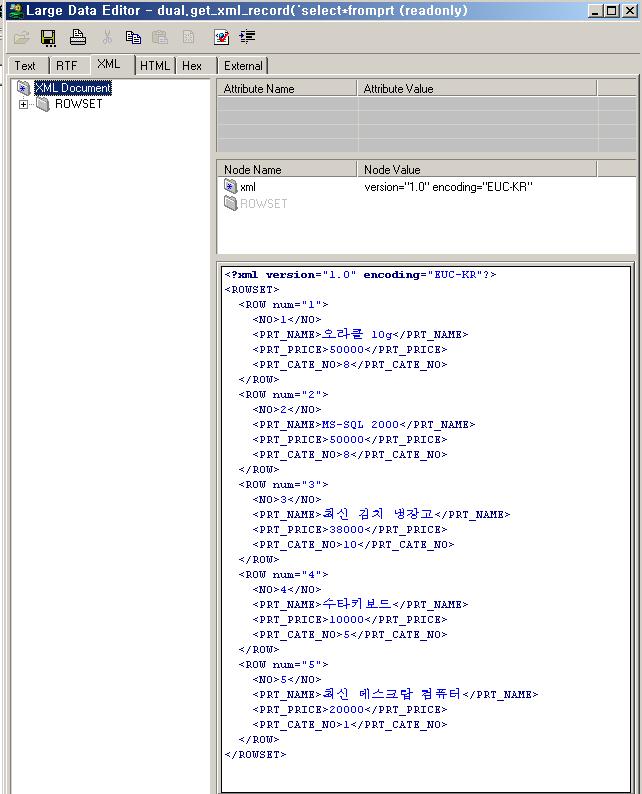
In these examples, the sales data that you will report on is held in the SH sample schema shipped with Oracle9i Database and Oracle Database 10g, whilst the vendor invoices data will be provided via an XML feed from your transactional application. To create your own report layout, download the SQL query and sample of the XML file here.
Defining an SQL-based Sales Analysis Report
The first report you will create will be the sales report, using data from the SH Sample Schema. To begin the process, you open up your Web browser and log on to XML Publisher Enterprise, so that you start to put together your report definition. After entering your username and password successfully, you view the XML Publisher Enterprise home page.

Down the left-hand side of the Web page is a tasks pane that contains links to create a new folder or report, or upload an existing report. On the right-hand side of the page is a set of sample reports shipped with XML Publisher Enterprise.
You click on the Create a new folder link to create a folder for the reports you are about to define, and call it “Sample Reports.” Grouping reports like this makes it easy to separate them out into subject areas, and you can later on specify which users and groups are able to access individual folders and reports.

You then navigate to the folder that you have just created, and click on the link to create a new report, which you call “sales report.” Once the report is created, you are presented with options to view, schedule, edit or view the execution history of the report.

Now that you have created the report, you need to edit the definition in order to specify the data model, any parameters the report might use and the report layout. To do this, you click on the Edit link under the report title. XML Publisher Enterprise then brings up a dynamic HTML interface that presents the report definition elements in a tree view.

An XML Publisher report definition comprises several elements:
- The data model, which refers to either a database query or an XML document
- The report template, which you will define later using XML Publisher Desktop
- Any parameters used by the report, and
- Any lists of values for the parameter drop-down lists
These four elements collectively form the report definition, which XML Publisher then holds in XML format on the application server mid-tier.
Next, you click on the Data Model node on the report tree view, click on the New button to create a new data model, and then select the JDBC data source that connects to your database. If one does not already exist, you will need to click on the Admin link at the top of the page to define a JDBC connection.

Once the data source is selected, you then press the New Query Builder button to choose the data items that will be returned from your database connection. The Query Builder gives you the ability to make a selection of database tables and columns using a graphical user interface.

Once you have made your data selection, you then add the join conditions and any other elements you would like to add to your query and then save it to XML Publisher Enterprise.

Now that you have defined your data model, it is time to layout your report template.
Report templates define how your data elements are arranged on the page, and unlike ad hoc query tools such as OracleBI Discoverer your template can be completely free form and include data from multiple queries. With XML Publisher, you define your report templates using standard desktop tools such as Microsoft Word and Adobe Acrobat, and the standard download of XML Publisher 5.6.2 includes an add-in to Microsoft Word called XML Publisher Desktop that automates much of the process of setting up the template. In these examples, you will use Microsoft Word and XML Publisher Desktop, an add-in to Microsoft Word, to define your templates. (A Flash demo that illustrates this process for a Word template is available here.)
Once you have installed XML Publisher Desktop, you will see an additional toolbar menu that provides access to XML Publisher functionality. As your first report is based on data accessed via an SQL query, you access the Data menu and then select Report Wizard.

You then step through the wizard, specifying the SQL query used to retrieve the data, the JDBC connection details of your database, and the name of the data source that you used when working in XML Publisher Enterprise

Once the wizard has completed, you are then presented with the default layout for your data items.

You can now use the formatting features in Microsoft Word to change the format of your table, add report headers and footers, change the fonts that are used, and add your organization’s branding. Although you can remove and reorder columns within the default report layout, for this report you decide to keep with the full set of columns as you intend to export the dataset later on into Microsoft Excel for further analysis.
You decide that this report would be even more effective with a chart to accompany it. Using XML Publisher Desktop this is a simple operation that is started via the Chart menu item on the Insert menu, which will then bring up the Chart dialog.

Using the Chart dialog, you specify a Vertical Bar Chart with Amount Sold grouped by Product Category.

Now, when you view your report template, a picture of a sample chart that represents your bar chart accompanies your table.

After previewing this template using the Preview menu item, you then save it to your PC as an RTF file ready for uploading to XML Publisher Enterprise.
To do this, you first of all click on the Layouts node of the report tree view, then click on New, and name your report layout.

Then, after clicking back on the Layouts node, you select the RTF file that contains your template and upload it to XML Publisher Enterprise.

Finally, just to test that your report works, you save the report definition, return to the report options and click on View to run the report.

Defining a Vendor Invoices Template Based On XML Data
The second report you wish to produce will take its data from an XML feed from your transactional system. Like your SQL-based report, the first step in creating this report is to log on to XML Publisher Enterprise to create a new report definition, which you name “Vendor Invoices.”

After entering the name of the report, as with the previous report you are then presented with options to view the report, schedule it, view the history of previous executions or edit its definition.

Next, as before, you click on the Edit link and begin the report definition process.
Using the Web interface, you first define the location of the feed that will provide your XML data, which in this case will be accessed via HTTP from your transactional application Web server.

If your report uses any parameters and any lists of values, you can add them at this stage. However your report does not use any parameters and so you click on the Layouts menu item and upload the report template you defined earlier.
Then, as with the sales report, you start XML Publisher Desktop so that you can define your report template. Unlike the sales report that was based on an SQL query, the vendor invoices report is based on an XML feed, and you therefore obtain an extract of this data feed as an XML document. As an alternative to an extract XML document, which may not contain all of the data elements that you might want to include in your template, you can instead base your template on an XML schema that fully defines the elements in your report, although of course this will not contain actual data and any previews you generate will contain data structures only.
For this template, you therefore initially load in your data using the XML Document entry in the XML Publisher Desktop Data menu.

Once XML Publisher Desktop confirms that the document is loaded, you can use the Insert menu to layout your template. Unlike the Report Wizard you used earlier, with XML data you are initially presented with a blank page, and it is up to you to add data items to the template.
For this template, you wish to list out the invoices grouped by the vendors that your organization deals with. To do this, you select Table/Form and then Advanced… from the Insert menu, and then individually select grouping items and table rows using the Insert Table/Form dialog.

Once you have selected your data items and grouped by vendor details, you can then format the resulting table, add your company branding, and then preview the results as a PDF file.

Then, once you are happy with the layout, you upload the template file to XML Publisher Enterprise, and run the report. This time, the report will take its data from the XML feed from your transactional application. Notice how the user can change the output format from HTML to PDF, XML, Microsoft Excel and XML.

Analyzing Your Sales Data
Some of your users may wish to further analyze their sales data to spot opportunities and uncover hidden trends. XML Publisher 5.6.2 Enterprise comes with an online analysis facility that gives your users the ability to analyze their data using just their Web browser.
To demonstrate this functionality, you navigate back to your sales report, run the report and then click on the Analyze button at the top right-hand side of your report. XML Publisher 5.6.2 Enterprise then presents you with a pivot table style interface that lets you drag and drop data elements onto a crosstab, in a similar style to an OracleBI Discover worksheet.

You drag the channel description field onto the Y-axis of the crosstab, and then drop the channel class item on top of it to nest the first item within the second. You do the same with Product Subcategory and Product Category, and drop Calendar Year into the Page Items area to allow users to “page through” years of data. Finally, you add Quantity Sold to the Data Items area and view the resulting page.

XML Publisher indexes and “rotates” the data from your report on the application mid-tier, and therefore there’s no extra load on your database or transactional system whilst you do this online analysis.
For users who would rather do their analysis using the familiar spreadsheet tool Microsoft Excel, the Excel Analyzer button starts your local copy of Microsoft Excel, installs a plug-in if it’s not already been downloaded, and then loads your report into an Excel worksheet. Using this plug-in, you can re-query the report using new parameter values, refresh the report with new data, and base additional worksheets off this data and include it in other calculations and graphs.
Report Scheduling and Distribution
Sometimes you might wish to schedule a report for later execution, or you might wish it to execute on a regular basis and distribute the results to a group of users. You wish to distribute your vendor invoice report on a weekly basis, and so you press the Schedule button at the top of the report to set this up. Before you do this though, you will need to have defined one or more delivery options using the Admin tab of XML Publisher 5.6.2 Enterprise.
To setup your schedule, you select one or more delivery destinations, which in the case of this report is an email message to the purchasing managers in your organization.

Using the Web interface, you give the scheduled job a name, and an email address to send notification through if the job should fail or complete with errors. The scheduler within XML Publisher 5.6.2 Enterprise gives you the option to run the job now, once in the future, or on a regular daily, weekly or monthly basis; you set the job up to run each Monday at 07:00 hours, with the report sent to an email distribution list and to yourself as a copy.
Granting Access to Users and Groups
The requirement from your organization is that only staff within the Purchasing Department should view the Vendor Invoices report, and other reports based on purchasing information, while sales reports should be viewable only by members of the Sales Department. Your online reporting application must reflect these security choices.
Within XML Publisher 5.6.2 Enterprise, individual users can belong to one or more roles, and roles can be granted access to one or more folders. This security can be made more granular by creating subfolders within other folders, and then using the copy report and paste report feature in XML Publisher 5.6.2 Enterprise to move your reports to the relevant subfolder.

Once your reports are in the correct folder, you then grant access to these folders to the relevant XML Publisher groups.

These roles, users and permissions are held internally within XML Publisher 5.6.2 Enterprise, but can be integrated with other LDAP servers.
Enhancing Your Templates
So far you have built two reports that are fairly simple to design and understand. You have used the wizards in Microsoft Word to lay out your template, and uploaded them to XML Publisher 5.6.2 Enterprise to be run online. But what if your requirements are more complex?
Most XML Publisher templates are created as RTF files which are then processed by the XML Publisher RTF Template Parser and converted into XSL-FO. When you design your report template using Microsoft Word, the wizards add data fields and other markup to your template using XML Publisher’s simplified tags for XSL expressions. These tags associate the XML report data to your report layout. If you are familiar with XSL and prefer not to use the simplified tags, XML Publisher also supports the use of pure XSL elements in the template.
In addition to Microsoft Word’s formatting features, XML Publisher supports other advanced reporting features such as conditional formatting, dynamic data columns, running totals, and charts. If you wish to include code directly in your template, you can include any XSL element, many FO elements, and a set of SQL expressions extended by XML Publisher. For more details, see the Oracle XML Publisher Enterprise User’s Guide that contains full details on how to extend XML Publisher templates.
Conclusion
XML Publisher 5.6.2 Enterprise is a complete environment for designing, building and running reports against both XML and SQL data. Using XML Publisher 5.6.2 Enterprise, you can design report layouts using familiar tools such as Microsoft Word and Adobe Acrobat, and deliver reports to your organization’s users using a secure, user-friendly Web-based environment.
Mark Rittman is a certified Oracle Database administrator and director of consulting at SolStonePlus, an Oracle partner based in the U.K. that specializes in business intelligence and data warehousing. He is the
Oracle Magazine Editors' Choice ACE of the Year 2005, is chair of the U.K. Oracle User Group Business Intelligence & Reporting Tools SIG, and runs a blog at
www.rittman.net.
출처 : 오라클